25 Sep A Brighter Smile Starts Here: How to Prevent Tooth Decay
A Brighter Smile Starts Here: How to Prevent Tooth Decay
By Island Hospital | September 25, 2024 12:00:00 PM
Medical Reviewer: Dr. Chang Chiew Sinn, Orthodontics
Tooth decay remains a significant oral health concern in Malaysia, with a staggering six out of ten adults requiring dental care due to this issue.
Based on the World Health Organisation’s 2022 Oral Health Report for Malaysia, this alarming statistic highlights the urgent need for enhanced oral health awareness and accessible dental services nationwide.
While the human mouth is home to over 600 bacterial species, only a small subset is directly responsible for tooth decay.
To prevent this, effective oral health management, including prioritising education and regular dental check-ups, can significantly reduce the risk of tooth decay and promote a lifetime of healthy smiles.
Let’s explore the strategies outlined in this article to prevent tooth decay!
Understanding Tooth Decay
Tooth decay, also called cavities, is a common dental problem caused when bacteria in the mouth break down sugary foods and starches, creating acids that erode the tooth’s enamel and dentin.
This process, combined with food debris and saliva, first forms plaque that clings to the teeth which will eventually lead to cavities.
It starts as a small spot on the tooth but can worsen, leading to a cavity or even a painful infection in the tooth’s centre.
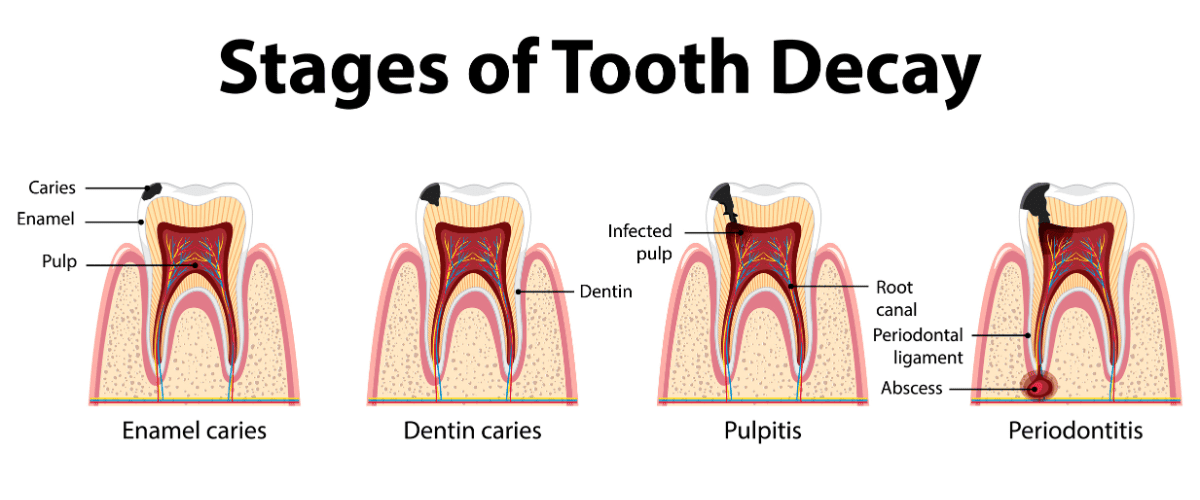
Photo by Freepik
Tooth Decay Symptoms
Early stages of tooth decay may not cause any noticeable symptoms in the beginning and may vary depending on the number of affected teeth and their location.
However, as the decay progresses, you may experience the following symptoms such as:
- Toothache
- Tooth sensitivity
- Visible holes or pits in your teeth (Cavities)
- Brown, black, or white stains on your teeth
- Bad breath or an unpleasant taste in your mouth (Halitosis)
- Swelling or pus around the affected tooth (Dental abscess)
Causes of Tooth Decay
Tooth decay results from a combination of factors that accumulate over time:
- Acid Erosion
Frequent exposure to acidic substances, such as acidic or carbonated drinks and stomach acid (in people with acid reflux), can weaken tooth enamel and increase the risk of decay. - Bacteria
Certain bacteria in the mouth, notably Streptococcus mutans, feed on sugars and starches in your diet. They produce acids that can erode the enamel of your teeth. - Diet
Consuming excessive amounts of sugary and starchy foods and drinks can provide fuel for the bacteria that cause tooth decay. - Dry Mouth
Saliva helps neutralise acids in the mouth and protect teeth from decay. Dry mouth, caused by certain medications (e.g. chemotherapy medications) or medical conditions (e.g. Sjogren’s syndrome), can increase the risk of tooth decay. - Genetics
Your genes can influence your teeth’s development and susceptibility to dental problems. However, other factors like poor oral hygiene, smoking, dry mouth, and not flossing can also contribute to cavities. - Poor Oral Hygiene
Not brushing your teeth twice a day, not flossing regularly, and not using mouthwash can allow bacteria and plaque to accumulate on your teeth.
A healthy diet is the cornerstone of good oral health. Discover how to incorporate nutritious foods into your daily routine in our article on Malaysia Health Plate.
Ways to Prevent Tooth Decay
Maintaining good oral and dental hygiene is detrimental to preventing cavities. Here are some recommendations to safeguard your dental health:
1. Floss daily
- Flossing helps remove food particles and plaque from between your teeth, where your toothbrush can’t reach.
- For thorough oral hygiene, it is best to floss before brushing your teeth with 8 to 10 strokes, up and down between each tooth.
- For easier manoeuvring, consider using an interdental brush or a water flosser (especially if you have braces or dental implants).
- Avoid using toothpicks to remove food particles, as they can damage your gums and increase the risk of infection.
2. Brush your teeth twice a day
- Brush your teeth at least twice daily, preferably after each meal, using a soft-bristled toothbrush to prevent gum irritation.
- Brush for at least two minutes each time at a 45-degree angle, reaching all surfaces of your teeth.
- Use gentle, circular motions and avoid scrubbing too hard, as it will cause gum recession.
3. Use a mouthwash
- Use a mouthwash that contains fluoride to prevent cavities.
- However, do not use it immediately after brushing your teeth, as it might wash away the fluoride from your toothpaste.
- Wait 30 minutes before eating or drinking after using a fluoride mouthwash.
4. Maintain a healthy diet and lifestyle
- Limit the consumption of sugary and starchy foods and drinks as they provide fuel for bacteria that can cause tooth decay.
- If you do consume sugary or starchy foods, rinse your mouth with water afterward.
- Certain foods and drinks, like fresh produce and unsweetened beverages, can help prevent cavities by stimulating saliva flow and removing food particles.
- Avoid tobacco and excessive alcohol as they can damage your teeth and gums, increasing your risk of tooth decay.
- Proper stress management is also essential to prevent the risk of tooth decay, as you may be more likely to engage in unhealthy behaviours, such as bruxism. This can lead to tooth wear and jaw pain.
5. Stay hydrated
- Drinking adequate amounts of water helps rinse away food particles and bacteria.
- The average recommended amount of daily water intake for healthy individuals is:
Age groups | Recommended amounts |
|---|---|
| Recommended amounts |
|
| Adolescents / Young adults |
|
| Adults |
|
| Senior citizens |
|
However, it should be noted that these amounts vary by individual and depend on their health status.
- You can also opt to drink at least a pint (~500ml) of fluoridated water each day to safeguard against tooth decay.
6. Consider sealants
- Dental sealants are a protective coating applied to the chewing surfaces of your teeth, especially molars, to help prevent cavities.
- Ideal candidates for dental sealants include:
- Children
Sealants are often applied to children’s teeth as soon as their permanent molars erupt, as they are more susceptible to cavities. - Adults with deep grooves or pits in their teeth
If you have teeth with deep grooves or pits, sealants can help protect them from decay. - Individuals at high risk of cavities
People who are prone to cavities, such as those with dry mouth or poor oral hygiene, may benefit from sealants.
- Children
7. Manage acid reflux
- If you have acid reflux, it can erode your tooth enamel. Talk to your doctor about ways to manage this condition.
8. Use fluoride treatments or products
Fluoride is a mineral that plays a crucial role in strengthening tooth enamel, making it more resistant to decay-causing acids.
It works by remineralizing weakened enamel areas, helping prevent cavities from forming.
Here are some common sources of fluoride you can incorporate into your dental hygiene regimen:
- Fluoride toothpaste
This is the most common way to get fluoride. It’s essential to choose a toothpaste that contains fluoride. - Fluoride mouthwash
Using a fluoride mouthwash can provide an extra layer of protection. - Fluoridated tap water
Many communities add fluoride to their tap water to promote dental health. - Professional fluoride treatments
Your dentist may recommend professional fluoride treatments, especially for children and individuals at high risk of decay.
9. See a dentist regularly
- Regular dental check-ups and cleanings are essential for maintaining good oral health. Your dentist can detect and treat early tooth decay or gum disease signs.
Discover the importance of teeth scaling for removing plaque and tartar to prevent chronic periodontal diseases. Learn about the procedure, benefits, and costs in our guide on teeth scaling.
Treatments for Tooth Decay
The treatment for tooth decay depends on the severity of the condition. Here are some standard treatment options:
Treatment options | Key Description |
|---|---|
| Fluoride treatments |
|
| Dental fillings | Dentists use fillings to repair cavities by removing the decayed portion of the tooth and filling the cavity with a material such as composite resin, amalgam, or porcelain. |
| Root canal treatment | This treatment is necessary when the decay has reached the tooth's pulp (the soft, living tissue inside the tooth). The procedure involves removing the infected pulp, cleaning the root canal, and sealing it to prevent further infection. |
| Extraction | In severe cases of decay, your dentist may need to extract the decayed tooth. |
Seeing a dentist at the first sign of tooth decay is important as early treatment can often prevent more serious complications.
Confidence Starts with a Fresh Smile!
Prevention is key when it comes to dental health.
Protect your teeth with effective tooth decay prevention strategies to save time, money, and discomfort by avoiding the escalation of toothaches or infections that will eventually affect your lifestyle.
At Island Hospital, our dedicated dental specialists offer personalised care, including root canal treatments and other dental services. We prioritise your well-being and strive to provide exceptional dental care for a better quality of life.
Our comprehensive dental screenings cater to individuals of all ages. Explore our exclusive Children’s Dental Screening and Golden Smile For Seniors packages to ensure optimal oral health.
Schedule your appointment today to discuss your oral health needs and explore other preventive dental services.
FAQ
Can tooth decay be fixed?
Yes, tooth decay can often be fixed, but the treatment depends on the severity of the decay.
- Early-stage decay: Can often be treated with fluoride treatments or fillings.
- More advanced decay: May require a crown or root canal treatment.
- Severe decay: In rare cases, extraction may be necessary.
It is important to see a dentist as soon as you notice any signs of tooth decay.
How can I get my teeth healthy again?
While it’s not possible to reverse enamel or bone damage, there are ways to strengthen your teeth and prevent further decay.
This process, known as remineralization, can be achieved through different ways such as lifestyle changes and home remedies.
Why are my teeth decaying so fast?
It is possible that there are several underlying causes that may quicken the pace of your tooth decay. That being said, it is essential to practise preventive measures to prevent this oral issue from worsening.
How do I differentiate between a stain and tooth decay?
While both stains and tooth decay can cause discoloration on your teeth, there are key differences to help you tell them apart:
Stains | Cavities |
|---|---|
| Tend to be more evenly spread and can affect multiple teeth. They often appear as a yellowish or brownish discoloration. | Usually appear as targeted discoloured marks, holes, or pits in specific teeth. |
| Typically do not cause pain or sensitivity. | Can lead to tooth sensitivity, pain, or even visible holes in the teeth. |
| Usually have a smooth surface. | Often have a rough or pitted texture. |
How long will a decayed tooth last?
A decayed tooth is a ticking time bomb. By neglecting it can lead to further complications, including damage to surrounding teeth and the jaw. The timeline for a decayed tooth to fall out varies depending on the severity of the damage.
Related Doctors
| Derived from | Complications |
|---|