20 Dec Preventing Vision Loss: A Guide to Diabetic Retinopathy Treatment
Preventing Vision Loss: A Guide to Diabetic Retinopathy Treatment
By Island Hospital | December 20, 2024 12:00:00 PM
Diabetes is a medical condition that can lead to a variety of health problems, including heart disease, kidney disease, and foot damage.
In severe cases where diabetes is not treated, high blood sugar levels can also cause vision loss, a condition known as diabetic retinopathy.
In Malaysia, where diabetes is a growing public health concern, diabetic retinopathy affects about 9% of the Malaysian population or an estimated 1.9 million people.
Despite increasing awareness and advancements in healthcare, many individuals need to be made aware of the risks associated with this condition and the importance of early detection and treatment.
Let’s explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for diabetic retinopathy, gaining a deeper understanding of this condition and how to prevent and manage it effectively.
Introduction to Diabetic Retinopathy
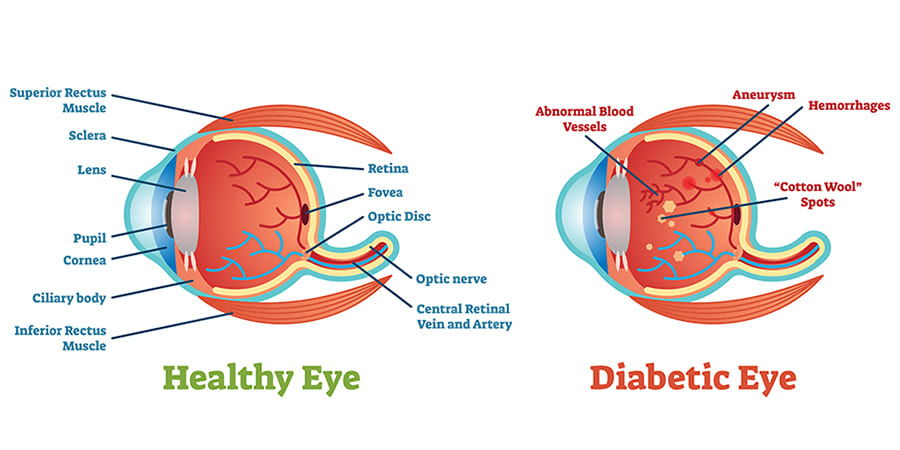
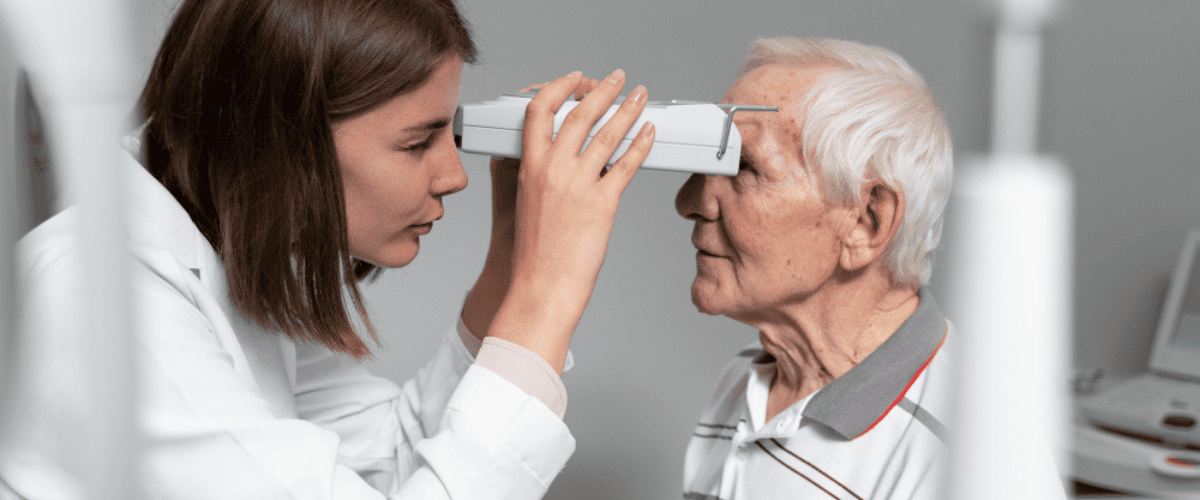
Photo by American Optometric Association
Diabetic retinopathy is a serious sight-threatening complication associated with diabetes that can lead to vision loss or even blindness. This medical condition usually affects both eyes.
Over time, diabetes can damage the blood vessels in the retina. This damage can cause these vessels to leak fluid or blood, which can then harm the retinal tissue – eventually leading to blurred or cloudy vision.
There are two types of diabetic retinopathy which are:
-
Non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy (NDPR)
This is the early stage of diabetic retinopathy, where symptoms are mild or non-existent. Individuals with NDPR have weakened blood vessels in their retina and tiny bulges called microaneurysms that may leak fluid into the retinal space, causing it to swell.
-
Proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR)
PDR is a more advanced stage of the disease where the retina is deprived of oxygen due to circulation problems. Consequently, new, fragile blood vessels form in the retina and into the vitreous, causing a blood leak into the aqueous space and resulting in cloudy vision.
Diabetic Retinopathy Symptoms
The early stages of diabetic retinopathy often have no noticeable symptoms. However, you may experience temporary changes in your vision, such as difficulty reading or seeing distant objects.
As the disease progresses, you might develop the following symptoms:
- Blurred or distorted vision
- Experiencing a dark or empty spot in the centre of your field of vision
- Seeing floating spots or streaks resembling cobwebs (eye floaters)
- Night blindness
While these spots might disappear on their own, immediate medical attention is essential. Untreated, these bleeds can lead to scarring in the back of the eye and potentially worsen over time.
Risk Factors
Individuals contracted with diabetes type 1, type 2, or gestational diabetes are susceptible to diabetic retinopathy.
Neglecting effective diabetes management over an extended period can significantly increase this risk.
Some factors that increase your risk of developing this condition are:
- Age and genetics
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- High tobacco use
- Poor blood sugar control
- Pregnancy
If you have diabetes, seeing an eye doctor regularly for eye exams is vital, as early detection and treatment can help prevent vision loss from diabetic retinopathy.
An ophthalmologist is responsible for diagnosing and treating amblyopia. Check out our article to learn what to expect and how to prepare for your visit!
Diagnosis and Tests
Early detection of diabetic retinopathy is crucial for preventing vision loss. Regular eye exams are essential for individuals with diabetes, regardless of whether they experience any symptoms.
Here are the common tests used to diagnose diabetic retinopathy:
1. Dilated Eye Exam
A comprehensive dilated eye exam is one of the most common and effective diagnostic tools for diabetic retinopathy.
In this exam, your doctor will dilate your pupils with eye drops to examine the back of your eye. This may cause temporary vision blur, which typically lasts only several hours.
They will look for signs of diabetic retinopathy, such as:
- Exudates: White or yellow deposits in the retina.
- Haemorrhages: Bleeding in the retina.
- Microaneurysms: Tiny, bulging blood vessels in the retina.
- Neovascularization: The growth of new, abnormal blood vessels in the retina.
2. Fluorescein angiography
This test involves injecting a dye into your bloodstream via your arm and taking pictures of your retina with a special camera. The dye helps pinpoint any abnormal blood vessels (e.g., blocked, broken, or leaking).
3. Optical coherence tomography (OCT)
OCT uses light to create cross-sectional images of the retina, allowing your doctor to measure the thickness of the retinal layers. This helps to detect early signs of diabetic retinopathy and assess the amount of fluid that has leaked into the retinal tissue.
OCT exams can also be used to monitor the progress of your treatment.
Treatments for Advanced Diabetic Retinopathy
To slow or halt the progression of diabetic retinopathy, treatment plans are tailored to the specific type and severity of the condition:
Early Diabetic Retinopathy
Individuals with mild or moderate NDPR may not require immediate treatment. However, regular eye exams are necessary to assess when intervention becomes necessary.
To enhance your diabetes management, collaborating with your endocrinologist to determine the most effective treatment strategies can significantly improve outcomes.
For mild or moderate diabetic retinopathy, effective blood sugar control can often slow the disease’s progression.
Advanced Diabetic Retinopathy
If you have diabetic retinopathy that is affecting or threatening your vision, the primary treatment options are:
| Eye Injections | A medication (e.g. anti-VEGF drugs or corticosteroids) will be injected into your eye to slow the disease’s progression and treat severe maculopathy that’s sight-threatening. |
| Laser Treatment (Photocoagulation) | It is employed to treat PDR and to stabilise certain cases of maculopathy by reducing swelling in your retina and shrinking or stopping leakage of new blood vessels. |
| Eye Surgery | If laser treatment is not feasible due to the advanced stage of retinopathy, a surgical procedure may be necessary to remove blood or scar tissue from the eye. A surgeon may remove a portion of the vitreous humour. |
| Steroid Eye Implants | Your doctor may recommend steroid eye implants if anti-VEGF injections are ineffective or unsuitable for you. A healthcare provider will inject an implant containing a steroid medication called dexamethasone into your eye after applying a local anaesthetic. Over the months, this medication will be slowly released, helping you improve your vision while reducing swelling. The implant eventually dissolves on its own, eliminating the need for removal. |
| Vitrectomy | For patients with diabetic retinopathy who experience cloudy vision due to leaking blood vessels, a surgical procedure known as vitrectomy may be recommended. During vitrectomy, a small incision is made in the eye to remove scar tissue and repair damaged blood vessels. |
Homecare and Management
Diabetic retinopathy is a leading cause of adult blindness, but patients can play a proactive role in their care, potentially mitigating its impact.
A self-care routine can help control symptoms and prevent disease progression. Incorporating these lifestyle adjustments can also improve your overall well-being:
- Exercise regularly (e.g. include aerobic exercises into routines)
- Maintain a healthy diet rich in foods that are nutritional for the eyes
- Manage your glucose levels
- Monitor your blood pressure and cholesterol levels
- Regulate your stress levels (e.g. include meditation sessions or yoga to relieve stress)
- Quit smoking
Don’t be fooled by misconceptions. Discover the truth about glaucoma in our informative article, “The Most Common Myths Surrounding Glaucoma.“
Take Control of Your Diabetes
Effective diabetes management is crucial for preventing diabetic retinopathy.
Work closely with your healthcare provider to maintain healthy blood sugar levels and reduce your risk.
At Island Hospital, our diabetic centre features a team of internationally recognised diabetes specialists offering comprehensive care for individuals with type 1, 2, and gestational diabetes.
We provide a wide range of services, including weight-loss therapy and surgery, to address the complex needs of patients with diabetes and related conditions.
Our commitment to excellence in advanced diagnostics, cutting-edge therapies, and compassionate support has earned us local and worldwide recognition:
A finalist for Malaysia’s Flagship Medical Tourism Hospital Programme
A place on Newsweek’s list of World’s Best Hospitals 2024
A place Global Health Asia Pacific Awards 2024
Time is of the essence when it comes to diabetes, as it can lead to other life-threatening issues.
Don’t let these symptoms worsen. Book your eye exam with us today to learn more about our treatment options.
FAQ
How do you stop diabetic retinopathy from getting worse?
You can lower your risk of developing diabetic retinopathy or slow its progression by effectively managing your blood sugar, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels. This often involves adopting healthy lifestyle habits, but some individuals may also need medication.
Can vision be restored after diabetic retinopathy?
The damage caused by diabetic retinopathy is often irreversible. While complete vision restoration is not always possible, specific treatments can help improve vision to some extent. Although treatments may not fully reverse the damage, your eye doctor can help prevent further vision deterioration.
What foods help diabetic retinopathy?
Vitamin A plays a crucial role in maintaining eye health, particularly night vision. Carrots, sweet potatoes, spinach, kale, and cantaloupe are sources of this vitamin.
Although vitamin A supplements are available, consuming a balanced diet is generally recommended to obtain this vitamin. Adequate vitamin A intake can contribute to overall eye health and potentially slow the progression of diabetic retinopathy.
Can you live an everyday life with diabetic retinopathy?
Regular eye exams and effective diabetes management can significantly reduce the risk of diabetic retinopathy and vision loss for many individuals.
Even if you experience vision loss, abundant resources, such as specially trained guide dogs, support you in adapting and maximising your remaining vision.
Related Doctors
| Derived from | Complications |
|---|