16 Jul 3 Most Common Types of Hepatitis in Malaysia
3 Most Common Hepatitis
By Island Hospital | March 7, 2025 4:33:40 PM
Over the past decade (2013 to 2023), Malaysia recorded 49,992 cases of Hepatitis B and 34,573 cases of Hepatitis C.
These statistics highlight the importance of early screening, timely treatment, and preventive vaccination for hepatitis, especially for those in high-risk groups.
In this article, we’ll explore the different types of Hepatitis virus, what causes them, the common symptoms of viral hepatitis, and the treatments available.
Note: For information about Hepatitis vaccination services in Penang and the price of the Hepatitis B vaccine at Island Hospital, please refer to the end of this article.
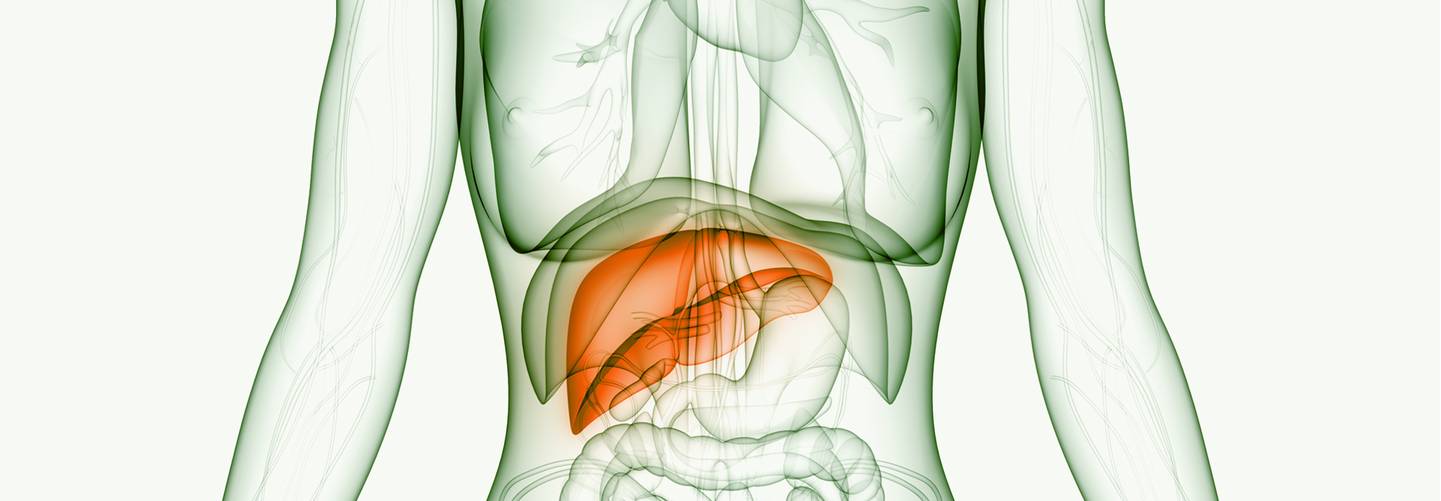
What is Hepatitis?
Hepatitis is a condition where the liver is inflamed. The liver is a vital organ that processes nutrients, filters the blood, and fights infections. When the liver is inflamed or damaged, its function can be affected.
The cause of hepatitis is usually a viral infection, although there are other possible causes of hepatitis as well.
These include autoimmune hepatitis and hepatitis that occurs as a secondary result of some medications, drugs, toxins, and heavy alcohol consumption. Autoimmune hepatitis is a disease that occurs when your body makes antibodies against your liver tissue.
Types of Viral Hepatitis
There are five types of viral hepatitis, and they are categorised into Hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E. These categories of hepatitis are each transmitted by different viruses. However, Hepatitis A, B, and C are the most common in Malaysia.
Hepatitis A is always an acute, short-term disease, while hepatitis B, C, and D are most likely to become on-going and chronic. Hepatitis E is usually acute but can be particularly dangerous in pregnant women.
Read our complete guide to liver disease to learn about the symptoms, treatment, and prevention of these diseases!
The Most Common Types of Hepatitis: A, B, and C
In this section, we’ll dive deeper into three types of hepatitis:
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A is an acute, and short-term disease caused by an infection with the hepatitis A virus (HAV).
How long does it last?
Symptoms may be relatively mild and go away in a few weeks, but an infection may result in a severe illness that lasts several months.
How is it transmitted?
Hepatitis A is spread when one ingests faecal matter (may be in microscopic amounts) from contact with food or drinks contaminated by faeces (at any point of growing, harvesting, processing, handling, and even after cooking) or stool from an infected person.
Who should be vaccinated?
All children aged 12–23 months and all children and adolescents 2–18 years of age who have not previously received hepatitis A vaccine (known as “catch up” vaccination).
Who is at risk?
- Tourists and travellers
- Men who have sexual relations with men
- Those who inject illegal drugs
- Occupational hazards (exposure)
- People who are homeless with no access to proper sanitation
How serious is it?
People who get hepatitis A usually recover completely and do not have lasting liver damage. In rare cases, and more common in older people and those with serious health issues, such as chronic liver disease, hepatitis A may cause liver failure and even death.
How is it treated?
Usually rest, adequate nutrition, and lots of fluids is recommended. Some people with severe symptoms will need medical care in a hospital.
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B can be acute or chronic, and caused by an infection with the hepatitis B virus (HBV).
How long does it last?
Hepatitis B can start as a mild illness, lasting a few weeks to six months, leading to a serious, chronic condition if one is not immunised, lasting 6 months or longer, or even a lifetime, possibly leading to serious illnesses such as cirrhosis and liver cancer.
How is it transmitted?
Hepatitis B is spread through exchange of blood or other body fluids – even in microscopic amounts, from an infected person with the hepatitis B virus to someone who is not infected.
The hepatitis B virus can also be transmitted from mother to child, sexual intercourse, sharing of equipment (needles, syringes etc), sharing of personal items (razors, toothbrush), and can spread easily due to poor infection control (accidental needle pricks) in healthcare facilities.
Who should be vaccinated?
Infants and children to adolescents who are younger than 19 years of age who have not been vaccinated, those who are sexually active and exposed to multiple partners and partners who have hepatitis B.
Who is at risk?
- Men who have sexual relations with men
- Healthcare workers who are at risk for exposure to blood or blood-contaminated body fluids on the job
- Haemodialysis patients and predialysis, peritoneal dialysis, and home dialysis patients
- Tourists and travellers to countries where hepatitis B is common
- People with hepatitis C
- People with chronic liver disease
- People with HIV
How serious is it?
A person’s risk of hepatitis B infection increases if he/she is exposed to multiple sex partners or with someone who is infected with HBV, or men having sexual relations with men as Hepatitis B spreads through contact with blood, semen or other body fluids from an infected person.
Sharing of needles during IV drug use may also put a person at risk. Living with someone who has a chronic HBV infection is also risky while a diseased mother can also infect a new-born child.
Healthcare workers are also at risk for exposure to blood. Blood-contaminated body fluids on the job pose a risk to infection as well. Besides that, travellers and tourists are also at risk, especially those travelling to regions with high infection rates of HBV, such as Asia, the Pacific Islands, Africa and Eastern Europe.
How is it treated?
An acute condition probably won’t need medical treatment. Instead, you will need plenty of rest, adequate nutrition, and lots of fluids and a healthy diet to support your body as it fights off the infection.
However, chronic hepatitis B, may need drug therapy. Usually, drug therapy is used only if you have active liver disease. You will need to take these medications every day that basically helps by slowing the virus’s ability to multiply in your system.
This also helps reduce swelling and liver damage. You will be regularly monitored for early signs of liver damage and liver cancer. Your healthcare provider will need to see you at least twice a year.
Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C can be acute or chronic, and caused by an infection with the hepatitis C virus (HCV).
How long does it last?
Hepatitis C can range from a mild illness, lasting a few weeks, to a serious chronic infection. Most people who get infected with the hepatitis C virus develop chronic hepatitis C.
How is it transmitted?
Hepatitis C is spread through exchange of blood or other body fluids – even in microscopic amounts, from an infected person with the hepatitis C virus to someone who is not infected.
The hepatitis C virus can also be transmitted from mother to child, sexual intercourse, sharing of equipment (needles, syringes, etc.), and due to poor infection control (accidental needle pricks) in healthcare facilities.
Who should be vaccinated?
There is currently no vaccine available for hepatitis C.
How serious is it?
More than 50% of people who get infected with the hepatitis C virus develop a chronic infection, while 5%-25% of people with chronic hepatitis C develop cirrhosis over 10-20 years.
How is it treated?
At present, there is not a recommended treatment for acute hepatitis C. Instead, people should be considered for treatment if their infection becomes chronic where there are several medications available to treat chronic hepatitis C. Treatments usually involve 8-12 weeks of oral therapy (pills) and cure over 90% of people with few side effects.
Did you know infection with the hepatitis B and C virus can lead to liver cancer? Learn more in our article on How to Prevent Liver Cancer.
Common Symptoms of Viral Hepatitis
Hepatitis signs and symptoms do not normally show until you have had the virus for a few weeks. While not everyone with hepatitis develops symptoms, one may experience:
- Fatigue
- Sudden nausea and vomiting
- Low-grade fever
- Abdominal pain on the upper right side of the stomach (by the liver)
- Joint pain
- Bowels that are clay-coloured
- Dark-coloured urine
- Loss of appetite
- Yellowing of the skin and the whites of your eyes (jaundice)
- Intense itching
Any symptoms of hepatitis need urgent medical attention.
How Are Hepatitis Infections Diagnosed?
Commonly, hepatitis infections are diagnosed through:
- Physical exams
- Blood tests
- Abdominal ultrasound
- Liver biopsy (if necessary)
If you’re looking to get tested, Island Hospital offers comprehensive Health Screening Packages, which include screenings for hepatitis B and C.
Hepatitis Vaccination in Penang
Vaccine for Hepatitis B is available at Island Hospital, Penang. The price for Hepatitis B vaccine at Island Hospital is as follows:
| 0 - 19 years old | RM30 | 3 doses (Total RM90) |
| 20 years old & above | RM60 | RM60 3 doses (Total RM180) |
Take Control of Your Hepatitis Health Today
At Island Hospital, we offer a complete hepatitis care journey under one roof – from prevention through vaccination, early detection via screening, to advanced treatment if needed.
Our state-of-the-art Health Screening Centre and specialised Gastroenterology department work seamlessly to provide comprehensive care using the latest medical technology.
Our commitment to excellence has earned us local and worldwide recognition:
- A finalist for Malaysia’s Flagship Medical Tourism Hospital Programme
A place on Newsweek’s lists of World’s Best Hospitals 2024
Trust Island Hospital as your dedicated partner for all hepatitis-related services – Schedule an Appointment Today!
Don’t Wait Until It’s Too Late – Get a Screening That Covers All The Bases

We’re offering our comprehensive Executive Health Screening Package at only RM760 – giving you a complete head-to-toe health assessment for peace of mind.
Our package features vital health screenings, including Cardiovascular Assessment, Full Blood Picture, Radiological Screening, Diabetes Screening, Kidney Function Test, and much more.
What’s Included in Your Screening Experience:
✔ Physical examination
✔ Complete medical report
✔ Consultation by Health Screening Physician/Specialist
✔ Choice of light refreshments
✔ Exclusive Island Hospital woven bag